Complete Linux/Unix Tutorial
I heartly invite you to Complete Linux/Unix Tutorial. This Linux guide is designed for both Beginners as well as experienced professionals in mastering Linux/Unix systems, I covered from basic commands to advanced system administration. Whether you are preparing for a role in DevOps or looking to bolster your system administration skills, this tutorial will encompass all essential topics.
What is Linux/Unix?
Linux is an open-source Operating system, it is similar to Windows, Mac and android Operating systems. Linux/Unix having comparable components, including the Kernel, Shell and programs.
Where is Linux Used?
The main applications for Linux are in Development environments, Servers, Cloud computing, Supercomputers, and Embedded systems. It is the foundation of Web Hosting, Data Centers, and Internet of Things devices due to its dependability, scalability, and security.
Introduction to Linux
Linux is a free and open-source operating system that is resilient and flexible. It is developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991. Linux, that’s well-known for its reliability, safety and flexibility, allows users to customize and improve their environment to suit specific needs.
What is Distribution?
An operating system composed of a number of applications built on the Linux kernel is called a Linux distribution. More than 500+ Linux distributions are available; a few of the most popular ones are listed here.
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Fedora
- CentOs
- openSUSE
- Arch Linux
- Solus
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
- Kali Linux
Architecture of Linux
Linux Architecture has the following components:
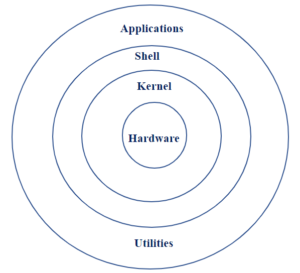
- Kernel: Kernal is the core part of Linux based Operating system. It acts as a bridge between software and hardware, managing system resources and ensuring different programs can run smoothly without conflicts. Different types of the kernel such as
- Monolithic Kernel
- Hybrid kernel
- Exo kernel
- Micro kernel
- Shell: Shell is the command-line interface of the Linux Operating system. It lets users type commands to interact with the system, like running programs, managing files and configuring settings. Different types of the Shell such as
- Bash
- Z Shell
- Korn Shell
- Fish (Friendly Interactive Shell)
- Hardware Layer: Hardware layer Consists of all the physical components of a computer, such as CPU, RAM, HDD/SSD and Input/Output Devices.
- System Libraries: System libraries in Linux are collections of pre-written code that applications use to perform common tasks, like file handling or network communication.
System Utilites: System utilities are built-in tools in Linux that help manage and maintain the system.
Basic Linux Commands For Beginners:
Here is some Basic Linux commands and their functions
| S.No | Command | Full Form | Function |
| 1 | ls | list | Displays information about files in the current directory. |
| 2 | pwd | present/current working directory | Displays the current working directory. |
| 3 | mkdir | make directory | Create a new directory. |
| 4 | cd | change directory | To navigate b/w different folders |
| 5 | rmdir | remove directory | Removes empty directory form the directory list. |
| 6 | cp | copy | Copy files from one to another directory. |
| 7 | mv | move | Move the files one to another directory. |
| 8 | rm | remove | Remove or Delete the files |
| 9 | uname | unix name | To get basic information about the OS |
| 10 | locate | locate | To find a file in the database. |
| 11 | touch | touch | Create an empty file |
| 12 | ln | ln | Create shortcuts to other files |
| 13 | cat | concatenate | Displays file content on terminal |
| 14 | clear | clear | Clear the terminal |
| 15 | grep | grep | Search for a specific string in an output or file |
| 16 | echo | echo | Print a test or string in the terminal |
| 17 | ps | process status | Display the process status in terminal |
| 18 | wget | wget | Download file form the internet. |
| 19 | man | manual | Access manual for all linux commands |
| 20 | df | disk free | Check the details of the file system |
| 21 | wc | word count | Check the lines, word count and characters in a file using different options |
| 22 | sort | sort | sort the file content |
| 23 | cal | calendar | view calendar in terminal |
| 24 | whoami | who i am | Displays the current users name |
| 25 | date | date | Displays the date |
| 26 | time | time | Displays the time |
| 27 | whereis | where is | view the exact location of any command typed after this command |
Linux File System
1. Logical File System: Acts as the interface between user applications and the file system, handling operations like opening, reading, and closing files.
2. Virtual File System (VFS): Provides a uniform interface for multiple physical file systems, enabling compatibility.
3. Physical File System: Manages the actual storage of data on disk, ensuring efficient data allocation and retrieval.
Linux File Hierarchy Structure
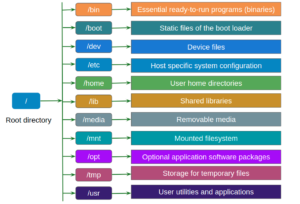
Linux File System Navigation Commands
File System navigation commands in linux are used to move around the directory structure, view contents, and manage file locations. Some common commands in below:
| Sl.No | Command | Function |
| 1 | pwd | show the current location |
| 2 | ls | list of files and folders |
| 3 | cd | change working directory |
| 4 | cd .. | Move to parent directory |
| 5 | cd ~ | go to the home directory |
| 6 | cd / | go to the root directory |
| 7 | find | search for files and directories |
| 8 | mkdir | create new folder |
| 9 | rmdir | remove folder |
| 10 | cp | Copy of a file in other location |
| 11 | mv | relocate files form one folder to another |
Package Management in Linux
Package management in Linux uses tools like apt, yum, or dnf to easily install, update, and remove software. It manages dependencies and keeps the system secure and up-to-date.
Package Managers and systemctl:
A package manager is a tool in Linux that simplifies managing software. It automates installing, updating, and removing packages—bundles of files like executables, libraries, and documentation—making software management efficient and organized.
User and Group Management in Linux
In Linux, managing users and groups includes tasks like creating, updating, or removing user accounts, setting permissions, and grouping users together. This ensures organized access control and strengthens system security.
User Management:
User management in Linux use to creating, maintaining, and controlling user accounts to manage access to system resources. It involves adding or removing users, assigning permissions, setting passwords, modifying user attributes, and organizing users into groups for streamlined access control and enhanced security. Tools like useradd, usermod, passwd, and groupadd are commonly used for these tasks, ensuring efficient management of user access and system resources.
Group management:
Group management in Linux involves creating, modifying, and removing groups to organize users efficiently. Groups are used to assign permissions and access rights collectively, simplifying resource sharing and security.
- Creating Groups: Using tools like
groupaddto add new groups. - Managing Users in Groups: Adding users to groups with commands like
usermod -a -G [groupname] [username]. - Deleting Groups: Removing groups with the
groupdelcommand. - Viewing Group Information: Checking group details in
/etc/group.
Linux Networking
In Linux Networking covers everything from setting up firewalls, monitoring traffic, and facilitating connection between devices and servers to configuring IP addresses and managing network interfaces.
- Configuring IP Addresses: Setting static or dynamic IPs using tools like
ifconfig,ip, or network configuration files. - Managing Network Interfaces: Enabling or disabling interfaces, configuring them, and using commands like
nmclior editing/etc/network/interfaces. - Setting Up Firewalls: Using tools like
iptablesorfirewalldto control incoming and outgoing traffic for security. - Monitoring Traffic: Analyzing network activity with tools like
tcpdump,netstat, orwireshark. - Connecting Devices and Servers: Establishing communication between devices using protocols like SSH, HTTP, FTP, or configuring DNS.
Configuration of Network Interface in Linux
The Network connection between a computer and another network, whether private or public, is known as a network interface. The network interface, also referred to as a NIC or Network Interface Card, is essentially a card that may be integrated into software rather than be physically present. For instance, some loopback addresses, like 127.0.0.1 (IPv4) and ::1 (IPv6), are bits of code put on the machine rather than being physically located.
There are two ways to Configure Network Interfaces in Linux.
The Command Line Method:
Dynamic Configuration: In Dynamic configuration, we can use tools like
dhclientornmclito automatically assign an IP address from DHCP.- Static Configuration: In Static Configuration Modify configuration files such as
/etc/network/interfacesor/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-*depending on the Linux distribution. You can use commands likeiporifconfigto assign a static IP. sudo nmcli con mod "enp0s3" ipv4.method auto
sudo nmcli con up "enp0s3" IPADDR=10.X.X.X
NETMASK=255.X.X.X.X
GATEWAY=10.X.X.X.X
ONBOOT=yes
DNS1=8.8.8.8
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Method:
- Network Settings: Use GUI tools provided by Linux distributions (e.g., NetworkManager or similar applications). These tools offer user-friendly options to configure network interfaces, set IPs, manage DNS, and apply firewall settings.
Networking Commands in Linux
Here are some commonly used networking commands in Linux:
| Command | Function |
ping (ping [hostname or IP] | Tests connectivity to a network or host. |
| ifconfig/ ip / ip a | Displays and configures network interfaces |
| netstat / netstat -a | Shows network connections, routing tables, and statistics. |
| curl/wget | Fetches data from URLs. |
| nslookup | Queries DNS information |
| traceroute | Traces the path packets take to a destination. |
| dig ( dig [domain Name] | Performs advanced DNS lookups |
| route / route -n | Configures and shows routing tables. |
| nmcli / nmcli con show | Manages network connections with NetworkManager. |
| scp / scp [source] [destination] | Securely transfers files between systems. |
The next documentation will include a comprehensive list of Linux commands along with their purposes and uses.
Are you thinking to learn more about Linux please visit the Linux official website.
Disclaimer: This website https://techcareerhubs.com/ gives information on job openings and fresh recruiting. This is solely for informational purposes. Candidates do not need to pay anyone for these jobs. We have no association with the organization. This information is derived from the company’s official website. The hiring process follows the organization’s recruitment procedure. We do not promise any jobs to the candidates.








1 thought on “Linux/Unix Tutorial 2025”