Top 10 AWS Projects: Discover 10 practical AWS project ideas for Cloud & DevOps Engineers. Perfect for hands-on learning, portfolio building, and real-world career success!
If you’re an aspiring or seasoned Cloud or DevOps Engineer, sharpening your AWS skills through hands-on projects is the fastest path to real-world expertise and a standout portfolio. In this blog, we present the Top 10 AWS Projects that are not only practical but also aligned with current industry demands. From automating infrastructure with Terraform, deploying CI/CD pipelines with Jenkins, and building serverless applications with AWS Lambda, to managing secure networks with VPC and running Kubernetes clusters using EKS, these projects will give you deep insights into real production environments. Whether you’re prepping for interviews, writing technical blogs, or aiming to land a top cloud role in 2025, these projects are your launchpad..
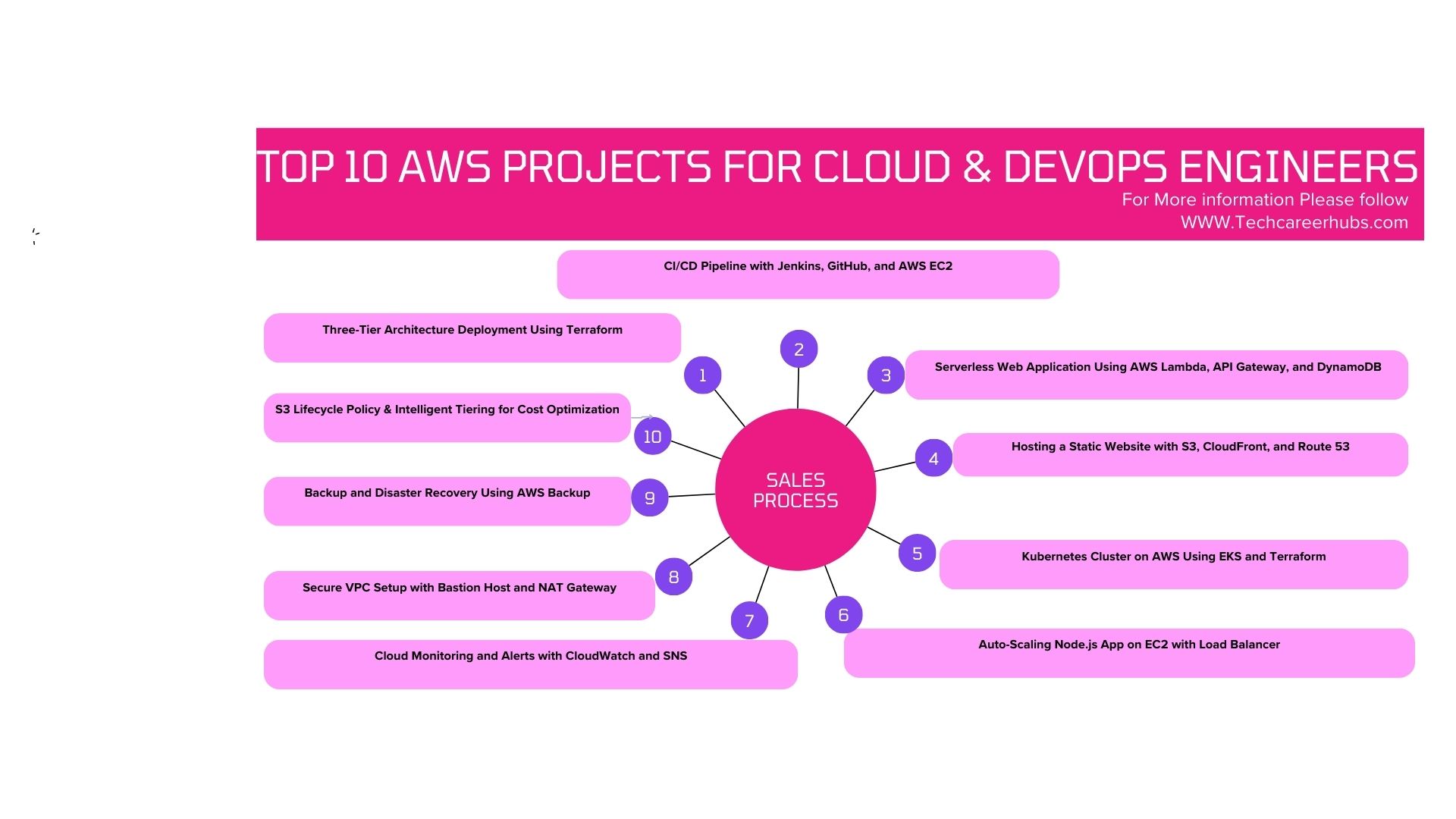
Top 10 AWS projects for cloud engineers
1. Three-Tier Architecture Deployment Using Terraform
What It Is:
A production-grade cloud infrastructure setup using Terraform to deploy a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with public and private subnets, EC2 instances, RDS databases, and an Application Load Balancer (ALB).
Use Cases:
Enterprise web applications requiring scalability, security, and high availability.
E-commerce platforms needing isolated tiers for web servers, app logic, and databases.
Technical Components:
VPC: Network segmentation for security.
EC2: Web/application servers in public subnets.
RDS: Managed MySQL/PostgreSQL in private subnets.
ALB: Distributes traffic across EC2 instances.
Steps to Build:
Write Terraform code for VPC, subnets, and route tables.
Deploy EC2 instances with Auto Scaling Groups (ASG).
Configure RDS with Multi-AZ for failover.
Set up ALB to route HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
Why It Matters:
Learn Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with Terraform.
Master AWS networking best practices.
Tools:
Terraform, AWS CLI, GitHub (for version control).
2. CI/CD Pipeline with Jenkins, GitHub, and AWS EC2
What It Is:
Automate code integration, testing, and deployment using Jenkins to pull code from GitHub, build with Maven, run tests, and deploy to EC2 instances.
Use Cases:
DevOps teams streamlining application delivery.
Startups needing rapid iteration cycles.
Technical Components:
Jenkins: Orchestrates pipeline stages.
GitHub: Source code repository.
EC2: Hosts deployed application.
Maven: Builds Java-based apps.
Steps to Build:
Configure Jenkins server on EC2.
Integrate GitHub webhooks for automatic triggers.
Write Jenkinsfile for build, test, and deploy stages.
Deploy artifacts to EC2 via SSH or AWS CodeDeploy.
Why It Matters:
Master continuous integration and zero-downtime deployments.
Tools:
Jenkins, Docker (optional for containerized builds), AWS CodeDeploy.
3. Serverless Web Application Using AWS Lambda, API Gateway, and DynamoDB
What It Is:
A cost-efficient serverless app where Lambda functions handle business logic, API Gateway manages HTTP requests, and DynamoDB stores data.
Use Cases:
REST APIs for mobile apps.
Event-driven microservices (e.g., file processing).
Technical Components:
Lambda: Executes code without servers.
API Gateway: REST/HTTP API endpoints.
DynamoDB: NoSQL database for scalable storage.
Steps to Build:
Create Lambda functions in Python/Node.js.
Design API Gateway routes (GET/POST/PUT/DELETE).
Configure DynamoDB tables with proper indexes.
Enable AWS Cognito for authentication (optional).
Why It Matters:
Learn event-driven architecture and pay-per-use pricing models.
Tools:
AWS SAM (Serverless Application Model), Postman (API testing).
4. Hosting a Static Website with S3, CloudFront, and Route 53
What It Is:
A low-cost, highly available static site hosted on S3, accelerated by CloudFront CDN, and routed via Route 53 DNS.
Use Cases:
Portfolio websites, blogs, or landing pages.
Marketing campaigns requiring global reach.
Technical Components:
S3: Bucket for HTML/CSS/JS files.
CloudFront: Content Delivery Network (CDN).
Route 53: Domain management and DNS routing.
Steps to Build:
Upload files to S3 and enable static website hosting.
Create CloudFront distribution with S3 origin.
Configure Route 53 to point domain to CloudFront.
Enable HTTPS via AWS Certificate Manager (ACM).
Why It Matters:
Master serverless hosting and global content delivery.
Tools:
AWS CLI, Terraform (for IaC), Hugo/Jekyll (static site generators).
5. Kubernetes Cluster on AWS Using EKS and Terraform
What It Is:
A managed Kubernetes cluster on Amazon EKS, deployed with Terraform, to run containerized microservices.
Use Cases:
Scalable microservices architectures.
Machine learning inference pipelines.
Technical Components:
EKS: Managed Kubernetes control plane.
EC2 Worker Nodes: Run application pods.
Helm: Package manager for Kubernetes apps.
Steps to Build:
Write Terraform code for EKS cluster and node groups.
Deploy sample apps using Helm charts.
Configure ALB Ingress Controller for external traffic.
Set up CloudWatch for cluster monitoring.
Why It Matters:
Gain expertise in container orchestration and cloud-native apps.
Tools:
kubectl, Helm, Prometheus (monitoring).
6. Auto-Scaling Node.js App on EC2 with Load Balancer
What It Is:
A Node.js application deployed on EC2 instances with auto-scaling to handle traffic spikes and an ALB for load distribution.
Use Cases:
Social media apps with variable traffic.
Real-time dashboards.
Technical Components:
Launch Template: Defines EC2 configuration.
Auto Scaling Group (ASG): Scales instances based on CPU/memory.
ALB: Routes traffic to healthy instances.
Steps to Build:
Create an AMI with Node.js and PM2.
Configure ASG with min/max instance limits.
Set up ALB with health checks.
Test scaling policies under simulated load.
Why It Matters:
Learn horizontal scaling and fault tolerance.
Tools:
AWS CloudFormation, Loader.io (for load testing).
7. Cloud Monitoring and Alerts with CloudWatch and SNS
What It Is:
A monitoring system using CloudWatch to track metrics/logs and SNS to send alerts via email/SMS.
Use Cases:
Proactive incident management.
Cost optimization via resource utilization tracking.
Technical Components:
CloudWatch: Metrics (CPU, memory), logs, dashboards.
SNS: Notification service for alarms.
Steps to Build:
Create CloudWatch alarms for EC2/RDS metrics.
Configure SNS topics and email subscriptions.
Set up Lambda to auto-resolve recurring issues (optional).
Why It Matters:
Master operational visibility and alert management.
Tools:
AWS SDK (for custom metrics), PagerDuty (integration).
8. Secure VPC Setup with Bastion Host and NAT Gateway
What It Is:
A network architecture with public/private subnets, a Bastion Host for secure SSH access, and NAT Gateway for private instance internet access.
Use Cases:
HIPAA/GDPR-compliant environments.
Databases needing isolation from public traffic.
Technical Components:
Bastion Host: Jump server in public subnet.
NAT Gateway: Allows private instances to fetch updates.
Security Groups: Restrict SSH/RDP access.
Steps to Build:
Design VPC with public/private subnets.
Deploy NAT Gateway in public subnet.
Configure Bastion Host with key-based SSH.
Test connectivity to private EC2 instances.
Why It Matters:
Learn network security and compliance best practices.
Tools:
Terraform, OpenVPN (for alternative access).
9. Backup and Disaster Recovery Using AWS Backup
What It Is:
Automated backup solutions for EC2, RDS, and EFS with cross-region replication for disaster recovery.
Use Cases:
Financial systems requiring RPO/RTO compliance.
Data protection against ransomware.
Technical Components:
AWS Backup: Centralized backup management.
S3 Glacier: Low-cost archival storage.
Steps to Build:
Create backup vaults and lifecycle policies.
Schedule backups for EC2/RDS resources.
Enable cross-region replication.
Test restore procedures.
Why It Matters:
Master data resilience and recovery strategies.
Tools:
AWS Backup CLI, AWS Organizations (for multi-account setups).
10. S3 Lifecycle Policy & Intelligent Tiering for Cost Optimization
What It Is:
Automatically transition S3 objects between storage classes (Standard, Glacier) based on access frequency.
Use Cases:
Media archives with rare access.
Log storage for compliance.
Technical Components:
S3 Lifecycle Rules: Define transition/expiration actions.
Intelligent Tiering: AI-driven storage optimization.
Steps to Build:
Create S3 buckets with versioning enabled.
Configure lifecycle rules for old logs/images.
Enable Intelligent Tiering for unpredictable access patterns.
Why It Matters:
Learn cost optimization and storage management.
Tools:
AWS Cost Explorer, S3 Analytics.
For More information about this follow the AWS office website.
[su_button url=”https://docs.aws.amazon.com/” background=”#ef312d” size=”10″]AWS official Documentation[/su_button]
Setting Up Your AWS Environment
How to Setup Your Development Environment for AWS | Introduction
Conclusion
These AWS projects help cloud engineers build job-ready skills in IaC, DevOps, serverless, and security. Start with foundational projects like static hosting or three-tier architectures, then advance to Kubernetes and disaster recovery. Document your work on GitHub and showcase it in interviews to stand out in the competitive cloud job market!
For more information stay tuned TechCareerHubs official website.